Research
Understanding the mechanism of viral pathogenesis
病原性細菌とは異なり、ウイルスは毒素遺伝子をもちません。
どのようにウイルスは人に重篤な症状を引き起こすのだろう?
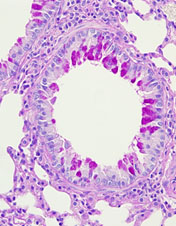
Multi-organ failure induced by viremia
SARS-CoV-2を含む、一部の呼吸器感染症ウイルスは肺胞から血中に侵入し、多臓器感染を引き起こします。
ウイルスはどのように基底膜や血管壁を乗り越えるのだろう?
What we know:
- Inflammatory response induces the leakage of blood vessels
- SARS-CoV-2, but not influenza virus, causes viremia
- Viremia is a hallmark of severe symptoms
Out of control of commensal bacteria
常在細菌は人に害を与えることなく、場合によっては体に利益をもたらして共生しています。しかし、インフルエンザウイルス感染を要因として、下気道で常在菌が異常増殖し、二次性細菌性肺炎を引き起こします。
ウイルスと常在細菌はどのように相互作用するのだろう?
What we know:
- Aging increases the risk of secondary bacterial pneumonia
- Virus infection impairs the phagocytic activity of alveolar macrophages
- Virus infection stimulates the migration of commensal bacterial from nasal cavity to alveoli
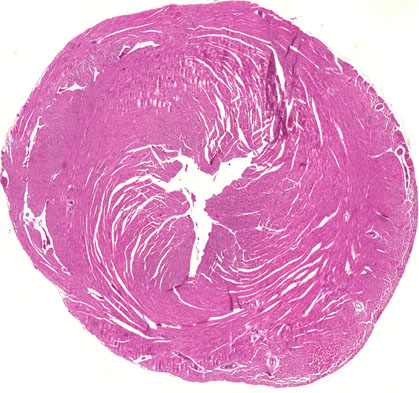
Cytokine storm leading to organ dysfunction
ウイルス感染やワクチン投与によって臓器局所で誘導される過剰な炎症反応は、全身に広がって他臓器にも心筋炎などの機能障害を引き起こします。
炎症反応が臓器間相互作用して疾患を引き起こすメカニズムは?
What we know:
- Seasonal influenza virus does not infect to hearts but induces myocarditis
- Sex difference; young males are at higher risk for myocarditis caused by mRNA vaccine
- No underlying disease; No host factors are identified
